Examples of investing cash flows include the cash outflow on buying property plant and equipment, the sale proceeds on the disposal of non-current assets and any cash returns received arising from investments. Solution As before, to ascertain the cash flow – in this case dividends paid – we can reconcile an opening to closing balance – in this case retained earnings. This working is in effect an extract from the statement of changes in equity. Deprecation reduces the carrying amount of the PPE without being a cash flow. The double entry for depreciation is a debit to statement of profit or loss to reflect the expense and to credit the asset to reflect its consumption.
Secure your fast, flexible financing today
Net income refers to the total sales minus the cost of goods sold and expenses related to sales, administration, operations, depreciation, interest, and taxes. The following exercise illustrates both the direct and indirect methods operating activities section. This topic is examined in much more depth in the FR examination than it is at FA. For example, in FA, an extract, or the whole statement of cash flow might be required in the multi-task questions but it could also be constructed as an OT question. FR, however, is more likely to ask for an extract from the statement of cash flows using more complex transactions (for example, the purchase of PPE using right-of-use asset leases).
Cash Flow From Operating Activities
Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. It is only in the calculation of the Cash Flow from Operations that the company accountants must make a choice between the Direct Method and the Indirect Method. The Cash Flow from Operations in the Cash Flow Statement represent Cash transactions that have to do with a company’s core operations and is therefore an extremely important measure of the health of a Business. Let’s say your company has an Accounts Payable balance of $200,000, a COGS of $1,000,000, and you’re analyzing over a year (365 days). However, excessive delays can harm supplier relationships and lead to missed discounts.
- The company’s current assets and current liabilities on 31 March 2019 are shown below.
- The profit on disposal of PPE of $500 ($2,000 – $1,500) would be adjusted for as a non-cash item under the operating activities (see later).
- Conversely, the cash flow direct method measures only the cash that’s been received, which is typically from customers, and the cash payments or outflows, such as to suppliers.
- If a company sells goods only for cash, then the amount of its sales revenue and cash received from customers will always be equal.
- It’s laborious for most companies to compile the information with this method.
- As noted above, IAS 7 permits two different ways of reporting cash flows from operating activities – the direct method and the indirect method.
Accounting Newbie?
The image below shows reported cash flow activities for AT&T (T) for the 2012 fiscal year. Using the indirect method, each non-cash item is added back to net income to produce cash from operations. In this case, cash from operations is over five times as much as reported net income, making it a valuable tool for investors in evaluating AT&T’s financial strength. The exact formula used to calculate the inflows and outflows of the various accounts differs based on the type of account. In the most commonly used formulas, accounts receivables are used only for credit sales, and all sales are done on credit.
Cash Paid for Insurance
The dividend income is received in cash, and there was no dividend receivable at the beginning or at the end of the year. Calculate the total amount of cash that ABC Company received during the year 2023 from interest and dividends. The accounts receivable at the beginning and at the end of the year are $25,000 and $35,000, respectively.
A bank overdraft should be treated as a negative cash balance when arriving at the cash and cash equivalents. Additional information During the year depreciation of $50,000 and amortisation the retirement savings contribution tax credit of $40,000 was charged to profit. In the following section, we demonstrate the calculations neededto assess the component pieces of the operating section using thedirect approach.
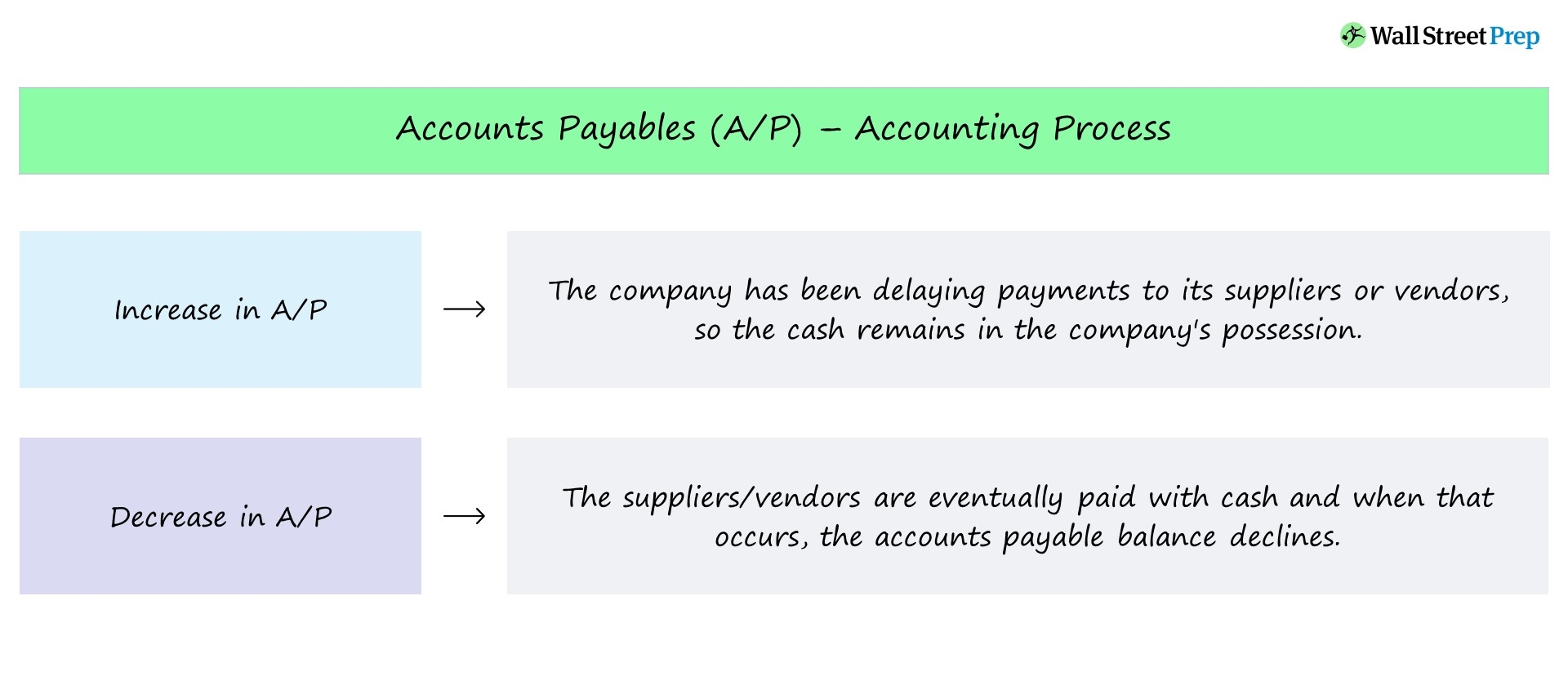
The reason is that the expenses are reported in the income statement on an accrual basis rather than a cash basis. In other words, expenses are reported in the period in which benefit is taken from the use of goods and/or services rather than in the period in which the actual cash payment is made to the providers of such goods and/or services. Financing activities cash flows relate to cash flows arising from the way the entity is financed. Entities are financed by a mixture of cash from borrowings (debt) and cash from shareholders (equity). Examples of cash flows from financing activities include the cash received from new borrowings or the cash repayment of debt. It also includes the cash flows related to shareholders in the form of cash receipts following a new share issue or the cash paid to them in the form of dividends.
Calculate the amount of dividends received by adjusting the dividend income shown in the income statement for the movement in the dividends receivable balances (DR) shown in the balance sheet. Cash flows are either receipts (ie cash inflows) and so are represented as a positive number in a statement of cash flows, or payments (ie cash outflows) and so are represented as a negative number in a statement of cash flows. It is these operating cash flows which must, in the end, pay off all cash outflows relating to other activities (e.g., paying loan interest, dividends, and so on). Operating activities are the transactions that enter into the calculation of net income. Examples include cash receipts from the sale of goods and services, cash receipts from interest and dividend income, and cash payments for inventory. Receipts from customers, combined with cash sales, were $800,000, payments to suppliers of raw materials $400,000, other operating cash payments were $100,000 and cash paid on behalf and to employees was $126,000.
Therefore, the amount of sales revenue generated during a period mostly differs from the amount of cash received from customers during that period. Solution (a) direct methodThe direct method is relatively straightforward in that all the data are cash flows so it is a case of listing the receipts as positive and the payments as negative. EXAMPLE 1 – Calculating the tax paidCrombie Co had a tax liability of $500 at 1 January 20X1. The tax liability at 31 December 20X1 is $900 and the tax charged in the statement of profit or loss was $1,000. A decrease in stock, debtors, or bills receivable (B/R) will increase cash flow from operating activities and increase stock.
In that initial reconciliation, the profit before tax is adjusted for income and expenses that have been recorded in the statement of profit or loss but are not cash inflows or outflows. For example, depreciation and losses on disposal of non-current assets, have to be added back, and non-cash income such as investment income and profits on disposal of non-current assets are deducted. T-accounts may also be used for each item in the balance sheet that affects the cash flow. For example, cash receipts from customers may be calculated using the t-account for accounts receivable.
The reconciliation itself is very similar to the indirect method of reporting operating activities. It stars with net income and adjusts non-cash transaction like depreciation and changes in balance sheet accounts. Since creating this reconciliation is about as much work as just preparing an indirect statement, most companies simply choose not to use the direct method.

